A Guide to Malolactic Fermentation
Malolactic Fermentation, also known as Secondary Fermentation or “Malo”, is the process in which Malic Acid in the wine converts to Lactic Acid.

What is Malolactic Fermentation?
As stated above, it is the process in which Malic Acid in the wine converts to Lactic Acid. The primary role of Malolactic Fermentation is to deacidify the wine which affects the sensory aspects of wine, making the mouthfeel smoother and it adds complexity to the flavor and aroma of the wine. The deacidification of the wine happens by converting the harsh diprotic malic acid into the softer monoprotic lactic acid. Nearly all red wines go through Malo while only a few whites, like Chardonnay and Viognier, do. One way to recognize if a wine has gone through Malo is if it has a creamy, buttery mid-palate texture. The buttery flavor comes from diacetyl, a by-product of the reaction.
What is Diacetyl?
Diacetyl is a flavor metabolite produced by lactic acid bacteria known as Oenococcus Oeni. Oenococcus Oeni is the main bacteria responsible for conducting Malo, due to its ability to survive the harsh conditions of wine. It is responsible for the production of the sensory aspects noted above. Malo can happen naturally, though often inoculated with the bacteria culture to jumpstart the process.
When does Malo take place?
Malolactic Fermentation can happen in two different ways, during primary fermentation or after. Amid fermentation, it is Co-Inoculation. After fermentation, it is Post-Fermentation Inoculation. Inoculation that takes place after alcoholic fermentation is the most common practice. When you add bacteria cultures like MBR31 after fermentation is complete, it jumpstarts the Malo process. Co-inoculation takes place at the start of alcoholic fermentation, which allows winemakers to focus on other things such as the improvement of flavor development.
What are the signs that Malo is in progress, and how do I know if it is finished?
The best way to identify malo in progress is bubbles! The malolactic activity can be detected by the presence of tiny carbon-dioxide bubbles. When the bubbles stop, Malolactic Fermentation is complete. This can take anywhere between one and three months.
What are the benefits of each method?
Firstly, the benefits of post-fermentation inoculation include better control of the start time duration of Malo. Lessened biogenic amine production leaves the wine unprotected by sulfite for a limited amount of time. This allows less potential for spoilage by other organisms. It reduces the incidence of excessive volatile acidity and enhances flavor profiles and complexity. The benefits of co-inoculation include lower levels of the inhibitory alcohol that are present at the start of Malo, and no need to apply external heating to the ferment due to the heat generated by the yeast fermentation. This results in faster completion of Malo. This means the wine can have sulfite added earlier and reduces the potential for the growth of spoilage organisms. Finally, a bonus is that bacteria added at the start of the yeast fermentation encounter a nutrient-rich environment.
Need assistance with your winemaking process?
Musto Wine Grape Company is here to help. We offer a wide variety of products and services to help you at any stage in your winemaking journey. Email winemaker@juicegrape.com or call us at (877) 812-1137 to speak with someone who can assist you.
How to do paper chromatography
Paper chroma-whata??
Paper chromatography: the way that home winemakers (and some commercial winemakers) check to see if their wines have completed malolactic fermentation or if they are still in the process of it. This is the time of year that winemakers are staying up on at what point their wine is at in the process of malolactic fermentation, because it will dictate when they can add potassium metabisulfite for the first time to their finished wine.
Why is it important?
Some wines should go through MLF for stylistic and stability reasons, whereas others should not.
How do I do it?
You’ll need to get a paper chromatography kit. This includes 3 acid standards (malic, lactic, tartaric), the solvent solution, chromatography paper, capillary tubes, and a plastic jar.
How accurate is it?
That’s the thing – it’s more qualitative than quantitative. Maybe it will show that there is still malic acid present, but that doesn’t mean it tells you how much is present, how long it’s been at this point, or if it’s even still decreasing anymore. It is qualitative in the sense that it shows: yes, acid X is present, or no, acid X is not present. If you’re searching for a more exact number or reference point you can send your samples in to a lab – if you’re looking to get an overall picture of whether or not your wine has any malic acid or lactic acid present, then using paper chromatography is the way to go.
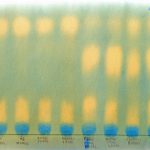
What does this stuff look like?
How do I do it?
- Collect your wine samples
- Draw a line 1-2 inches from the bottom of the paper using a pencil (pen will not work)
- Mark with an X or dot where you will place the samples.
- Use capillary tubes (one for each sample – don’t mix them up) to draw up a very small sample of the the standards (malic, lactic, and tartaric) and then the wine samples and drop a very small amount of the liquid onto the paper. You will notice it will spread out once it hits the paper so be sure not to drop too much liquid. Less is more here.
- Let the dots dry and repeat 3 times. This will make it easier to read down the road.
- Roll the paper up and staple either side without the paper overlapping onto itself.
- Pour a small amount of paper chromatography solvent solution into the bottom of the plastic jar. Be careful to not inhale this. Place the stapled paper, sample side touching the solution, into the jar. Screw the lid on and let sit for ~8 hours, or enough time for the solvent to reach from the bottom to the top of the paper.
- Take the paper out (carefully) and let it air dry until the entire sheet turns blue and yellow dots are clearly visible.
- Match up where you see specific acid dots with the wine samples and you can detect if malic and/or lactic acid is present in each sample.
Helpful hints
You will likely need to run this test at least a couple of times to see the decline in MLB and confirm its completion
Be sure not to add any potassium metabisulfite to your wine until MLF has completely finished!
Use space heaters or a warm room for wines undergoing MLF to help speed the process along
Collect your test samples







Recent Comments