Recent Posts
Archives
- October 2025
- August 2025
- June 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- November 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- September 2022
- August 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- September 2015
- August 2015
- April 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- September 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- March 2014
- June 2013
- July 2012
Categories
potassium metabisulfite
New Product Spotlight: Effergran

Introducing Effergran, the effervescent granulated potassium metabisulfite that’s your wine’s best friend during aging! This powerhouse product is a potent antioxidant and antimicrobial agent, designed to protect your wine by rapidly releasing SO2, minimizing oxidation, and ensuring a stable aging process.
Adding Effergran to your wine is not just effective—it’s a bit of a show! Imagine the satisfying fizz of an Alka-Seltzer tablet in water, but for your wine. As soon as Effergran hits the surface, it bubbles and dissolves quickly, effortlessly distributing SO2 throughout your wine. No pump overs, no hassle—just a seamless, thorough integration that keeps your wine in top condition.
Elevate your winemaking process with Effergran, where efficiency meets a touch of fun, all while maintaining the highest standards of professionalism. Cheers to better aging and exceptional wines!
Potassium Metabisulfite: Product Spotlight
What is Potassium Metabisulfite?

Potassium Metabisulfite is an antioxidant and sanitizer, and has several uses in winemaking. After crushing and de-stemming, it is used to help kill off any spoilage bacteria and natural yeast that may be present on the grapes or equipment. It also helps to preserve wine, specifically protecting it against oxidization.
Throughout the entire winemaking process, it’s important to measure your SO2 levels and adjust as needed to improve and lengthen the preservation of your wine. The exact amount needed to be effective is entirely determined by the pH of the wine. Also, free SO2 levels fall faster in a wooden barrel versus in glass or stainless steel tanks, so make sure you manage your SO2 levels very closely.
How do I use it?
If you are adding Potassium Metabisulfite to your must, the proper amount is ¼ teaspoon per 5 gallons of must. If you are making an SO2 sanitizing solution, add 8 teaspoons for every 1 gallon of water. Place into a spray bottle for quick and easy use. After cleaning your equipment and again before use, spray the solution generously and shake off/let any extra solution drip dry.
Potassium Metabisulfite has a shelf life of about one year if you are using it to add to your wine. If you have some that is over a year old, no worries! It still functions as a sanitizer, just make sure you separate and label each to avoid any mix ups.
Where can I get it?
You can find and purchase Potassium Metabisulfite here. Need assistance in using SO2, whether adding to your wine or sanitizing your equipment? Give us a call at (877) 812 – 1137 to speak with a sales associate who can help you!
Follow us on Instagram here and like us on Facebook here. For Virtual Winemaking Classes click here.
Free SO2: When and How
Protecting your wine with free SO2
Keeping the required amount of free SO2 in your wine is one of the important post-fermentation care steps you’ll need to stay on top of. While some people decide not to add SO2 (which is a personal preference, though we at Musto Wine Grape definitely recommend keeping the proper amount of free SO2 in your wine at all times), others choose to keep their wine protected by using it diligently.
Why we add it
To keep the wine protected. KMS serves as an antimicrobial and antioxidant and as such is a very important part in keeping your wine out of harm’s way. Without it, your wine can go bad very quickly.
How to test free SO2
Aeration oxidation method, manual ripper method, Vinmetrica, Hanna titrator, titrets
When to add it
- During crush (to kill off any unwanted native yeast)
- When fermentation has completed (be sure that MLF has completed as well, if that’s the goal)
- During aging. Example: Each month many winemakers will test SO2, make any SO2 adds if needed, and then top it off.
How to add it
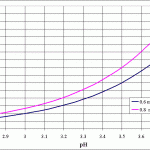
You’ll need to get potassium metabisulfite, if you don’t already have it. You may prefer to use campden tablets, which is fine too. Make sure it says potassium metabisulfite rather than sodium metabisulfite. The easiest way to figure out how much free SO2 you’ll need to add is to know your pH, first of all. Then you’ll need to decide if you’re using .8 or .5/6 molecular SO2. .8 is usually used for white wines, whereas .5 is used for red wines. Measure your free SO2 if you have a way of doing so. Then use the graph below to figure out what the target free SO2 is. From there you will likely choose an easy-to-use online resource such as wineadds.com to find out exactly how many grams of potassium metabisulfite should be added. Mix it with a small amount of water to ensure it can become completely incorporated into the wine.
*Remember: just knowing your target free SO2 in ppm does NOT tell you how many grams you will be adding. You need to figure that out as a second step, with an online SO2 calculator*
Now that you have a solid understanding of why, how, and when you add meta, you may want to delve into some deeper questions, such as…
Why do I need to keep adding meta? If I add a certain amount shouldn’t it stay at that number?
This is a great question. There are a lot of variables that go into answering this in as cohesive a way possible, and this could really be a topic in and of itself. Let’s keep it simple here: there are two measurements of SO2 in wine: free and bound. The free SO2 is what is actively protecting the wine, whereas bound SO2 is what has already tacked on to other compounds within the wine and as such is no longer able to actively protect it in the same way. Both are important numbers, but if a winemaker is only checking one, it’s going to be free. Over time free SO2 can become bound to various acids, solids, sugars, bacteria, yeasts, etc., that are present in the wine, which is why this number will not necessarily stay constant, especially immediately.
Why does pH affect how much SO2 I need to add?
A rule of thumb to remember is that higher pH = higher free SO2 requirement. Lower pH = lower free SO2 requirement. The chart below demonstrates the amount of free SO2 required base don the pH of the wine. This is just one of the many reasons that checking and knowing your wine’s pH is critical.
Do I need to measure total SO2 as well?
Knowing this number is important, but not as crucial as knowing your free SO2. It’s also a little less accessible of a test to run, which is why most home winemakers don’t choose to pursue knowing the total SO2 of their wines. It is possible to overadd SO2 and have the total SO2 be higher than desirable which can be problematic, so be sure to keep a running log and closely track how much you have added from the beginning of the wine’s life onward.
The Winemaker’s Think Tank: Vol 5 – Is Malocatic necessary in White Wines if it has not been inoculated?
What’s the Winemaker’s Think Tank?
Every Thursday we will post about a few frequently asked questions that our winemaker has answered. If you have a winemaking question you would like to have answered, please email us at support@juicegrape.com and we will try to get into next week’s post. Cheers! 🙂
Is Malocatic necessary in White Wines if it has not been inoculated?
When considering the stability of a white wine in preparation for bottling, sugar and microbial stability are of great importance. After fermentation, if MLF is not purposefully inoculated by the winemaker, the addition of Lysozyme may be considered as to retard any naturally present MLF bacteria from beginning to ferment. If the level of SO2 is kept up to is suggested level (contingent upon pH), the Lysozyme may not be needed as the SO2 will prevent the bacteria from fermenting. If the winemaker is trying to use a low amount of sulfites in their wine, I would suggest the use of Lysozyme to inhibit any bacterial growth.
Equally as important, is the use of sterile filtration. If the wine is processed through a sterile filter (.45µ), bacterial and yeast cells should be eliminated. This will physically prevent the bacterial spoilage of the wine. If the winemaker chooses to back sweeten the wine, this filtration will also help prevent any refermentation within the bottle. When it comes to back sweetening, I also always recommend chemical as well as physical sterilization of the wine to prevent fermentation and off aromas to develop within the bottle. Potassium sorbate may be used on any wine that has not gone through malolactic fermentation. If it is used on a wine that has undergone MLF, remaining MLF bacteria can begin to metabolize the sorbate, resulting in a strong geranium odor. In my experience, I typically add sorbate and sterile filter the wine, then bottle, without the addition of Lysozyme. I am meticulous about the level of SO2 remaining above the suggested amount , and I typically add an additional 10ppm before bottling to ensure prolonged sterility within the bottle.
While you certainly can conduct a chromatography test upon the wines to detect the presence of acid, both malic and lactic exist naturally within the grape, so the chromatography test will not be especially helpful when looking at a wine that has not gone through MLF. As long as you keep a vigilant watch upon your sulfur dioxide levels and pH, and use sorbate when sweetening, you should be fine.
We hope this information helps with your winemaking. If you have any follow up questions or winemaking questions in general, please email us at support@juicegrape.com.
The Winemaker’s Think Tank: Vol 4 – What is the best way to sanitize my equipment?
What’s the Winemaker’s Think Tank?
Every Thursday we will post about a few frequently asked questions that our winemaker has answered. If you have a winemaking question you would like to have answered, please email us at support@juicegrape.com and we will try to get into next week’s post. Cheers! 🙂
What is the best way to sanitize my equipment?
It is important to differentiate between cleaning, sanitizing, and sterilizing. Cleaning is removing any dirt, grape debris, or build-up from your equipment. Sterilizing is the process via heat or chemicals of eliminating all micro-organisms, which is nearly impossible in a home winemaking environment. Sanitizing is the goal for home winemakers. Sanitizing is the removal of harmful micro-organisms from the winemaking equipment. This will give the winemaker the healthiest environment possible for their wine. One of the most chemically and cost effective ways to sanitize winemaking equipment is by using potassium metabisulfite. Potassium metabisulfite works best in an acidic environment. To create a strong sanitizing solution, mix 2 tbsp. of citric acid and 1 tbsp. of potassium metabisulfite with 5 gallons of warm water. Mix all of these in a 6 gallon pail. You can now use this solution to sanitize all of your equipment. Submerge or rinse all of the equipment in this solution. This solution will sanitize the equipment of any harmful bacteria that could spoil the wine. Any tool, vessel, or hose that touches the wine should be rinsed thoroughly with the solution to prohibit contamination.
Also, check out our Youtube Video where our Bootcamp Professor Frank Renalid weighs in on sanitation
We hope this information helps with your winemaking. If you have any follow up questions or winemaking questions in general, please email us at support@juicegrape.com.
Archives
- October 2025
- August 2025
- June 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- November 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- September 2022
- August 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- September 2015
- August 2015
- April 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- September 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- March 2014
- June 2013
- July 2012
Copyright © 2026. All Rights Reserved.










Recent Comments